Supporting Therapy Selection For Cancer Patients
EPI-CALL™ is a second-generation comprehensive molecular profiling test that provides epigenomic analysis on top of genomic information offered by existing service providers. By leveraging bulk RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq), Whole Transcriptome Sequencing (WTS), EPI-CALL™ is the first epigenomic profiling test that provides clinical insights and supports therapy selection for cancer patients.
A patient has been diagnosed with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) and the clinician is exploring potential cancer treatment options.
The clinician can now refer to fusion genes associated with CML. For example, if the BCR-ABL gene fusion is reported, it indicates the presence of BCR-ABL fusion proteins, which are known to drive the growth and survival of leukemia cells. In response, the clinician may opt to offer the drug Imatinib (Gleevec) as the targeted therapy. Imatinib specifically targets and inhibits BCR-ABL fusion proteins to control the proliferation of cancer cells.
A patient has been diagnosed with late-stage gastric cancer and the clinician is exploring potential IO treatment options. However, it is uncertain how the patient might respond to this treatment of choice.
The clinician can now refer to APS that predicts the patient’s response to IO. If the APS suggests a high probability of response to IO, the clinician may opt for IO as the primary treatment.
Alternatively, if the APS indicates a low probability of response to IO, the clinicians may consider chemotherapy or a combination of therapies as the treatment plan. In this way, APS can enable the clinician to make well informed treatment plans.
A patient has been diagnosed with breast cancer; the clinician is exploring potential cancer treatment options.
The clinician can now refer to the expression levels of genes associated with breast cancer. For example, if the patient is HER2*-negative and yet HER2 gene expression is higher than the cancer-specific median, the clinician may consider trastuzumab, a HER2-specific antibody, as the targeted therapy to inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
*HER2 = Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2
A patient has been diagnosed with ovarian cancer and the clinician is exploring potential cancer treatment options.
The clinician can now refer to the alternate isoform expression levels of genes associated with ovarian cancer. For example, if the patient is BRCA2-negative and yet the alternate isoform expression level of BRCA2 gene is higher than the normal tissue baseline, it could suggest that the intended function of the gene is impacted, thereby leading to the loss of tumor suppressor functions of BRCA2 proteins. In response, the clinician may consider Lynparza (olaparib), a PARP inhibitor, as a targeted therapy to block the growth and spread of cancer.
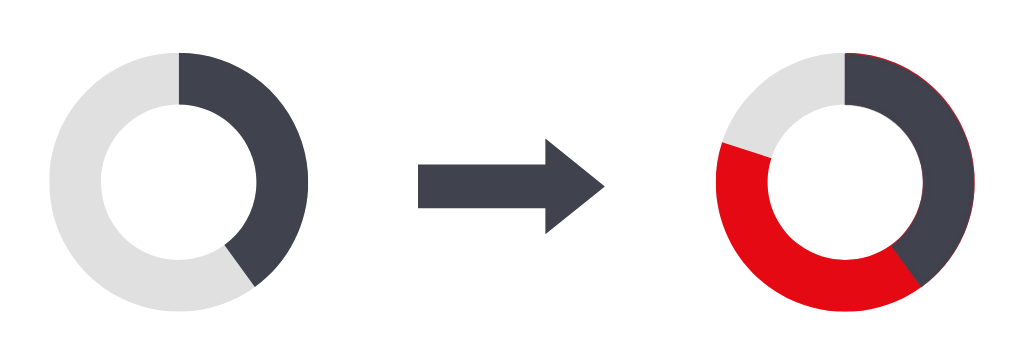
Genomic changes account for less than 50% of cancer cases; epigenomic profiling provides more information and better characterises cancer molecular profiles.
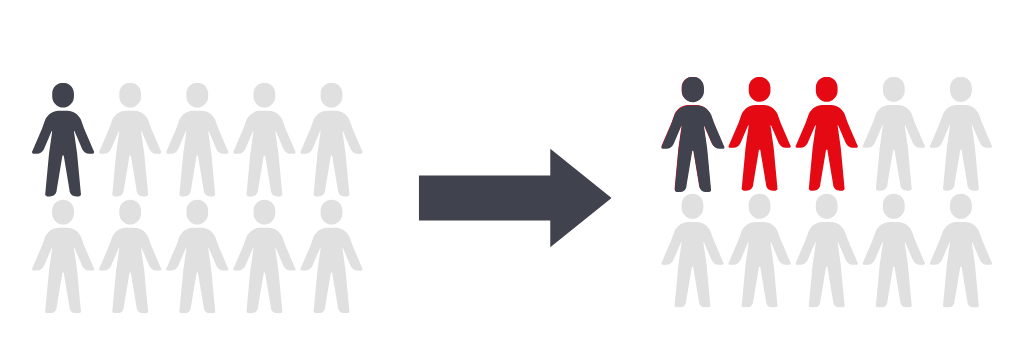
EPI-CALL™ can potentially identify up to 30% of IO responders by acting independently to existing prognostic biomarkers.
(CAR-T, cellular therapy, etc.)
(Level 3 Clinical Evidence)
A patient has been diagnosed with breast cancer; the clinician is exploring potential cancer treatment options.
The clinician can now refer to the expression levels of genes associated with breast cancer. For example, if the patient is HER2*-negative and yet HER2 gene expression is higher than the cancer-specific median, the clinician may consider trastuzumab, a HER2-specific antibody, as the targeted therapy to inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
*HER2 = human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
A patient has been diagnosed with ovarian cancer and the clinician is exploring potential cancer treatment options.
The clinician can now refer to the alternate isoform expression levels of genes associated with ovarian cancer. For example, if the patient is BRCA2-negative and yet the alternate isoform expression level of BRCA2 gene is higher than the normal tissue baseline, it could suggest that the intended function of the gene is impacted, thereby leading to the loss of tumor suppressor functions of BRCA2 proteins. In response, the clinician may consider Lynparza (olaparib), a PARP inhibitor, as a targeted therapy to block the growth and spread of cancer.
A patient has been diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and the clinician is exploring potential cancer treatment options.
The clinician can now refer to fusion genes associated with CML. For example, if the BCR-ABL gene fusion is reported, it indicates the presence of BCR-ABL fusion proteins, which are known to drive the growth and survival of leukemia cells. In response, the clinician may opt to offer the drugimatinib (Gleevec) as the targeted therapy. Imatinib specifically targets and inhibits BCR-ABL fusion proteins to control the proliferation of cancer cells.
A patient has been diagnosed with late-stage gastric cancer and the clinician is exploring potential immunotherapy (IO) treatment options. However, it is uncertain how the patient might respond to this treatment of choice.
The clinician can now refer to Alternate Promoter Score (APS) that predicts the patient’s response to IO. If the APS suggests a high probability of response to IO, the clinician may opt for IO as the primary treatment.
Alternatively, if the APS indicates a low probability of response to IO, the clinicians may consider chemotherapy or a combination of therapies as the treatment plan. In this way, APS can enable the clinician to make well informed treatment plans.
Interested in working with us? Drop us a note below and we’ll get back to you as soon as we can.
enquiry@auristone.com
LaunchPad @ one-north
73 Ayer Rajah Crescent, #02-19 Singapore 139952