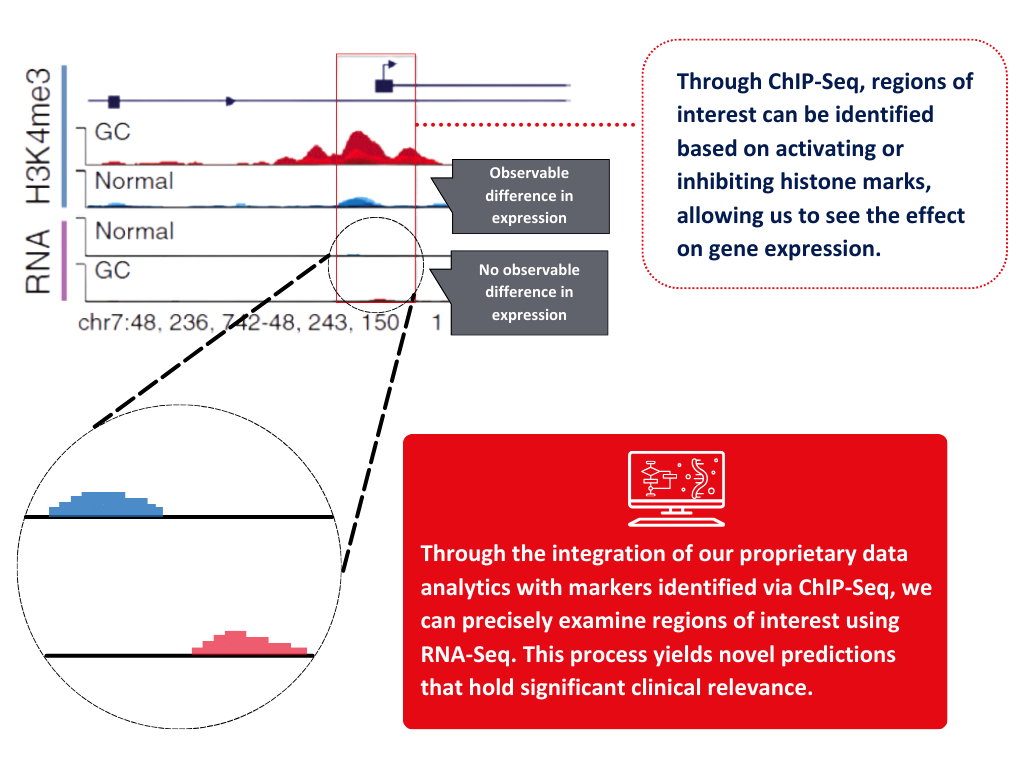
We utilise epigenomics to provide complementary insights to existing genomic information
Epigenomics examines modifications in gene expression that occur independently of changes in the DNA sequence. It focuses on exploring the mechanisms that influence gene regulation, which leads to downstream effects on gene expression. Unlike genomics, which studies the DNA sequence itself, epigenomics studies reversible modifications that impact gene activity without alteration of the underlying DNA sequence, rendering them undetectable through genomic assays.
Two of the most characterised epigenomic modifications are DNA methylation and histone modifications. DNA methylation involves the addition of methyl groups to DNA bases, primarily cytosines, while histone modifications encompass chemical alterations to histone proteins, changing the chromatin structure and influencing gene expression levels.
Auristone’s core technology centres around histone modifications while most other epigenomic companies focus on DNA methylation.